Factors Affecting Electricity Prices
Many Factors Impact Energy Prices, electricity prices generally reflect the costs to build, finance, maintain, manage, and operate power plants and the electricity grid (the complex system of power transmission and distributions lines) and to operate and administer the utilities that supply electricity to consumers. Some utilities are for-profit, and their prices include a return for the owners and shareholders.
Some key factors that affect the price of electricity include:
Some key factors that affect the price of electricity include:
- Fuels - Coal is relatively inexpensive while natural gas tends to be more costly.
- Power Plants - Construction and maintenance costs are greater for some kinds of power plants than others.
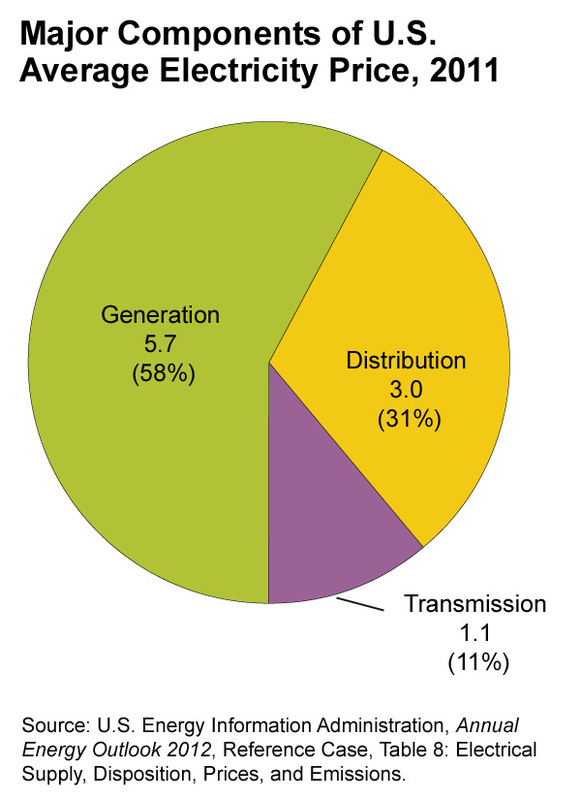
- Transmission and Distribution - Maintaining and using the transmission system to deliver electricity contributes to the cost of electricity.
- Weather Conditions - Rain and snow can provide water for hydropower generation. Extreme heat can increase the demand for electricity for cooling. Extreme cold can increase the demand for natural gas which in turn increases the cost of electricity.
- Regulations - In some states, prices are fully regulated by Public Service Commissions, while in others there is a combination of unregulated prices (for generators) and regulated prices (for transmission and distribution).
- Supply and Demand - This is the primary factor that influences fuel and electricity prices, as it does in all open markets. The demand for the commodity versus how much is available for purchase. Supply and demand are influenced by many variables.
- Load Factor - is defined as the average load divided by the peak load in a specified time period.
|
Electricity Prices Are Usually Highest in the Summer
The cost to generate electricity actually changes minute-by-minute. However, most consumers pay rates based on the seasonal cost of electricity. Changes in prices generally reflect variations in electricity demand, availability of different generation sources, fuel costs, and plant availability. Prices are usually highest in the summer because more expensive generation is added to meet the higher demand. Electricity Prices Vary by Type of Customer Prices are usually highest for residential and commercial consumers because it costs more to distribute electricity to them. Industrial consumers also use more and can take their electricity at higher voltages so it does not need to be stepped down. These factors make the price of power to industrial customers closer to the wholesale price of electricity. Electricity Prices Vary by Locality Prices vary by locality due to the availability of power plants and fuels, local fuel costs, and pricing regulation and structures. In 2010, annual average electricity prices ranged from 25.1 cents per kWh in Hawaii to 6.2 cents per kWh in Wyoming. State Electricity Profiles include annual prices other statistics for each state. |